Google如何处理网页
source : ahrefs.com
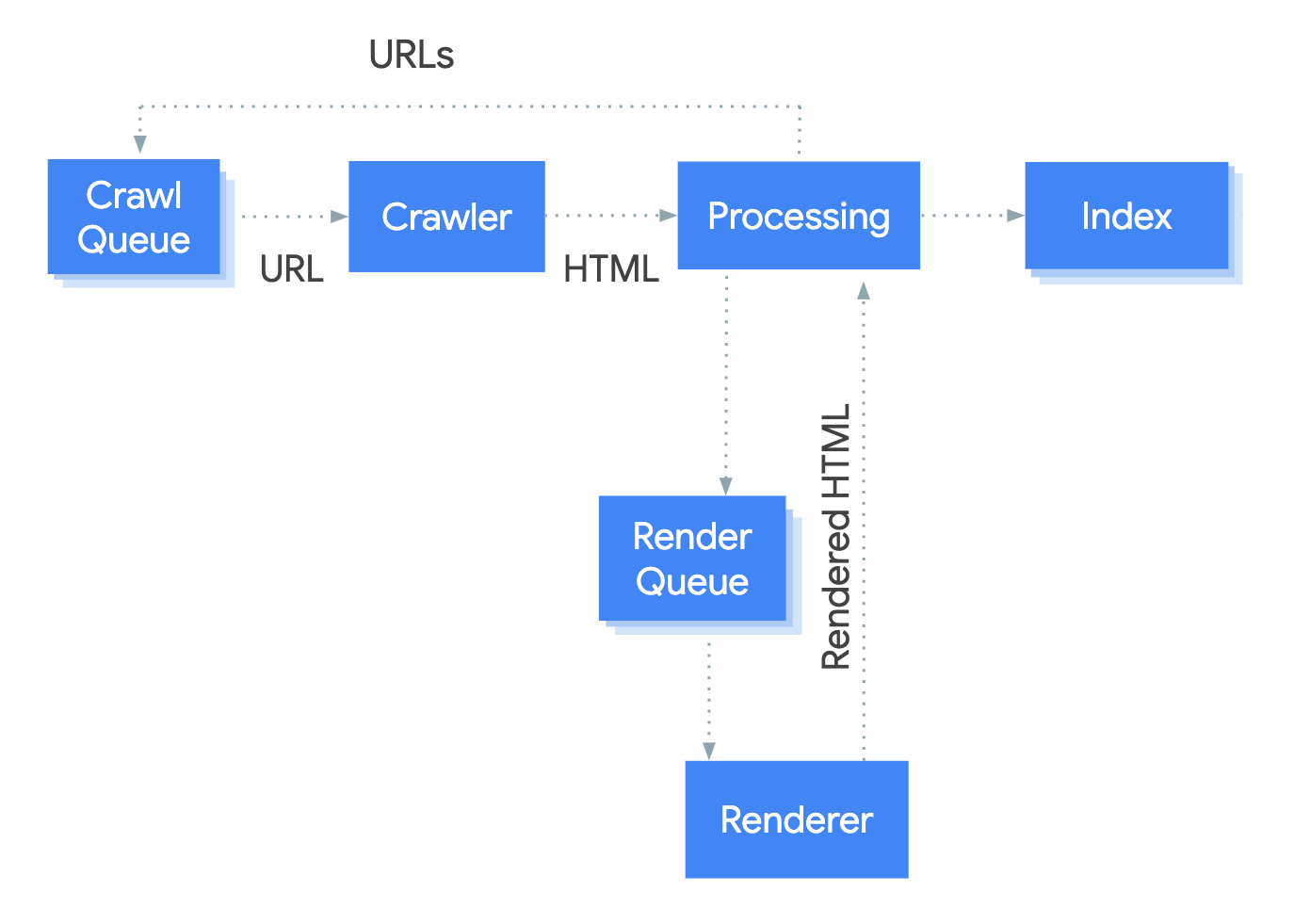
- Crawling - Googlebot sends GET requests to a server for the URLs in the crawl queue and saves the response contents. Googlebot does this for HTML, JS, CSS, image files, and more.
- Processing - This includes adding URLs to the crawl queue found within
<a href>links within the HTML. It also includes queuing resource URLs (CSS/JS) found within<link>tags or images within<img src>tags. If Googlebot finds a noindex tag at this stage, the process stops, Googlebot won't render the content, and Caffeine (Google's indexer) won't index it. - Rendering - Googlebot executes JavaScript code with a headless Chromium browser to find additional content within the DOM, but not the HTML source. It does this for all HTML URLs.
- Indexing - Caffeine takes the information from Googlebot, normalizes it (fixes broken HTML), and then tries to make sense of it all, precomputing some ranking signals ready for serving within a search result.
单页面应用SPA中的SEO
As the name implies, a SPA literally consists of a single HTML page sent down from the server. This page is just a shell, SPA framework like Vue focus on updating the body tag.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/vite.svg" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Vue</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="module" src="/src/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>相关链接
On This Page